Topic history of sony company: Explore the remarkable journey of Sony, a visionary company that revolutionized technology and entertainment, shaping the modern digital world from its inception in 1946 to its current global dominance.
Table of Content
What is the founding date of the Sony company?
The founding date of the Sony company is 1946.
- In 1946, Masaru Ibuka started an electronics shop in Shirokiya, a department store building in the Nihonbashi area of Tokyo.
- The company started with a capital of 190,000 yen and approximately 20 employees.
READ MORE:
Founding and Early Innovations
Sony\"s history began in 1946, post-World War II, when Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita founded Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo (Tokyo Telecommunications Engineering Corporation). Their vision was to create a company that would be a trailblazer in the field of electronics. Operating initially in a bomb-damaged department store building in Tokyo, their first product was a rice cooker, reflecting their dedication to meet immediate post-war domestic needs.
- Their early efforts soon shifted towards telecommunications and audio technology.
- In 1950, they released Japan\"s first tape recorder, the Type-G, marking a significant step in Sony\"s journey towards becoming an audio-visual electronics giant.
- Their commitment to innovation led them to develop smaller, high-quality consumer products.
The company\"s first major international success came with the transistor radio in 1955. The TR-55, Sony\"s first commercially successful transistor radio, catapulted the brand into global recognition. This success was built on the back of their earlier TR-52 model, which, while not as successful, laid the groundwork for future innovations.
- Their pursuit of compact and portable devices continued with the introduction of the world\"s first portable transistor TV, the TV8-301, in 1960.
- This period also saw the introduction of the iconic Walkman in 1979, revolutionizing the way people listened to music on the go.
Throughout these early years, Sony\"s pioneering spirit and commitment to quality and innovation established the foundations for its future as a global leader in electronics and entertainment.

Diversification and Expansion
During its journey from a small electronics shop to a global conglomerate, Sony has shown remarkable growth and diversification. After changing its name from Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo to Sony in 1958, the company started expanding its reach and portfolio. One of the first major steps was the establishment of Sony Corporation of America in 1960, marking Sony\"s serious entry into the international market.
Innovations were not just limited to electronics. Sony introduced the world\"s first non-projection type all-transistor and portable television, the Sony TV8-301, in the same year. By 1961, Sony had launched the world\"s first compact transistor VTR, PV-100. Another significant development was the launch of the Trinitron color television in 1968, which played a crucial role in establishing Sony as a leading TV manufacturer globally.
The 1970s and 1980s saw Sony diversifying into various other sectors. The iconic Walkman was released in 1979, changing the way people listened to music. This was followed by the introduction of the world\"s first Compact Disc player, the Sony CDP-101, in 1981, in collaboration with Philips. Sony\"s expansion wasn\"t limited to electronics; it entered the entertainment industry with the acquisition of CBS Records in 1988 and Columbia Pictures in 1989.
Entering the 21st century, Sony continued to innovate and expand. It played a major role in the development of the Blu-ray Disc format, which was released in 2006. Alongside electronics, Sony also made significant strides in the entertainment sector with its subsidiaries Sony Music Entertainment and Sony Pictures Entertainment. The company also ventured into the financial sector in Japan and the internet service providing through So-net.
However, the journey wasn\"t always smooth. Sony faced several challenges, including a period of stagnation and a fading brand name. Despite these challenges, Sony\"s diversification strategy, coupled with its innovative spirit, has played a significant role in shaping the company into the multifaceted conglomerate it is today.

Technological Milestones
Sony, originally named Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo, has a long history of technological innovations that shaped the consumer electronics industry. From its early days, Sony has been at the forefront of technological advancement.
- In 1955, Sony introduced the TR-55, the company\"s first transistor radio, marking the beginning of its journey in the consumer electronics market.
- 1960 was a significant year with the release of the world\"s first portable transistor TV, the Sony TV8-301.
- 1961 saw the launch of the world\"s first compact transistor VTR, the PV-100, followed by the revolutionary Trinitron color television in 1968.
- The 1970s and 1980s were marked by groundbreaking products like the Betamax videocassette recorder in 1975 and the Walkman in 1979, which changed the way people consumed media.
- Sony\"s innovation continued in the digital age with the introduction of the world\"s first Compact Disc player, the CDP-101, in 1981, in collaboration with Philips.
- 1991 was another landmark year with the release of the first commercial lithium-ion battery, a significant advancement in rechargeable battery technology.
- Entering the 21st century, Sony played a vital role in developing the Blu-ray Disc format, which was released in 2006, setting new standards for high-definition optical disc formats.
These milestones not only reflect Sony\"s commitment to innovation but also highlight its influence in shaping the technology and consumer electronics industries globally.

Challenges and Rebranding
Sony, a giant in the electronics and entertainment industries, has faced its fair share of challenges, leading to significant rebranding and strategic shifts. These challenges, while daunting, were pivotal in reshaping Sony\"s approach to business and innovation.
- In the mid-2000s, Sony faced significant setbacks with some of its proprietary formats like the Betamax, MiniDisc, and Memory Stick. These formats, while innovative, struggled against more universally adopted standards.
- The company also faced considerable controversy in 2006 with a massive recall of laptop batteries due to safety concerns, marking one of the largest computer-related recalls in history.
- Despite these challenges, Sony continued to innovate, notably with the development and launch of the Blu-ray optical disc format in 2006, which emerged victorious in the high-definition optical disc format war against Toshiba\"s HD DVD.
- Rebranding efforts included the introduction of the BRAVIA name in 2005 for its range of high-definition LCD televisions, projection TVs, and home cinema products, as Sony strived to maintain its position as a leading television manufacturer.
- The PlayStation line, especially with the release of the PlayStation 3 in 2006, was a significant part of Sony\"s strategy, despite the high costs associated with its advanced technology and Blu-ray capabilities.
These challenges and subsequent rebranding efforts reflect Sony\"s commitment to overcoming obstacles through innovation and strategic adaptation, securing its place as a leader in the global market.

_HOOK_
Present Day Sony
As of the present day, Sony Group Corporation, formerly known as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo and Sony Corporation, stands as a significant player in the global market. Headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan, Sony has diversified its portfolio extensively to include a wide range of products and services.
- The company\"s product line includes advanced cameras, computer hardware, consumer electronics, films, music, robots, semiconductors, telecommunications equipment, TV shows, and video games.
- Sony\"s services encompass sectors like advertising, banking, credit finance, financial services, insurance, and network services.
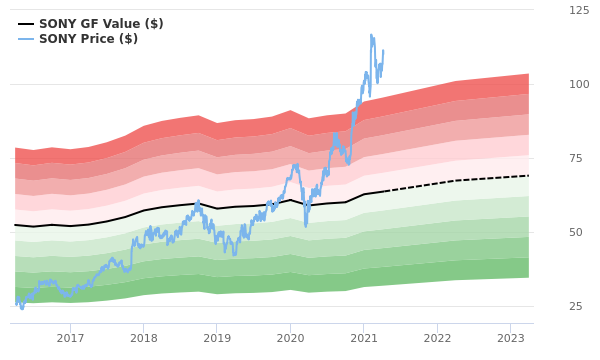
- In terms of revenue, Sony has shown a strong financial performance with an increasing trend in recent years.
- The conglomerate employs a significant number of people globally, reflecting its extensive operations and influence in various industries.
- Sony\"s subsidiaries include notable names such as Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Music Japan, Sony Semiconductor Solutions, and Sony Corporation of America, among others.
- The company holds a dominant position in the image sensor market, being the largest manufacturer with a substantial market share.
- In the entertainment sector, Sony\"s presence is marked by its involvement in the production of films and music, with subsidiaries like Sony Pictures Entertainment and Sony Music Entertainment playing key roles.
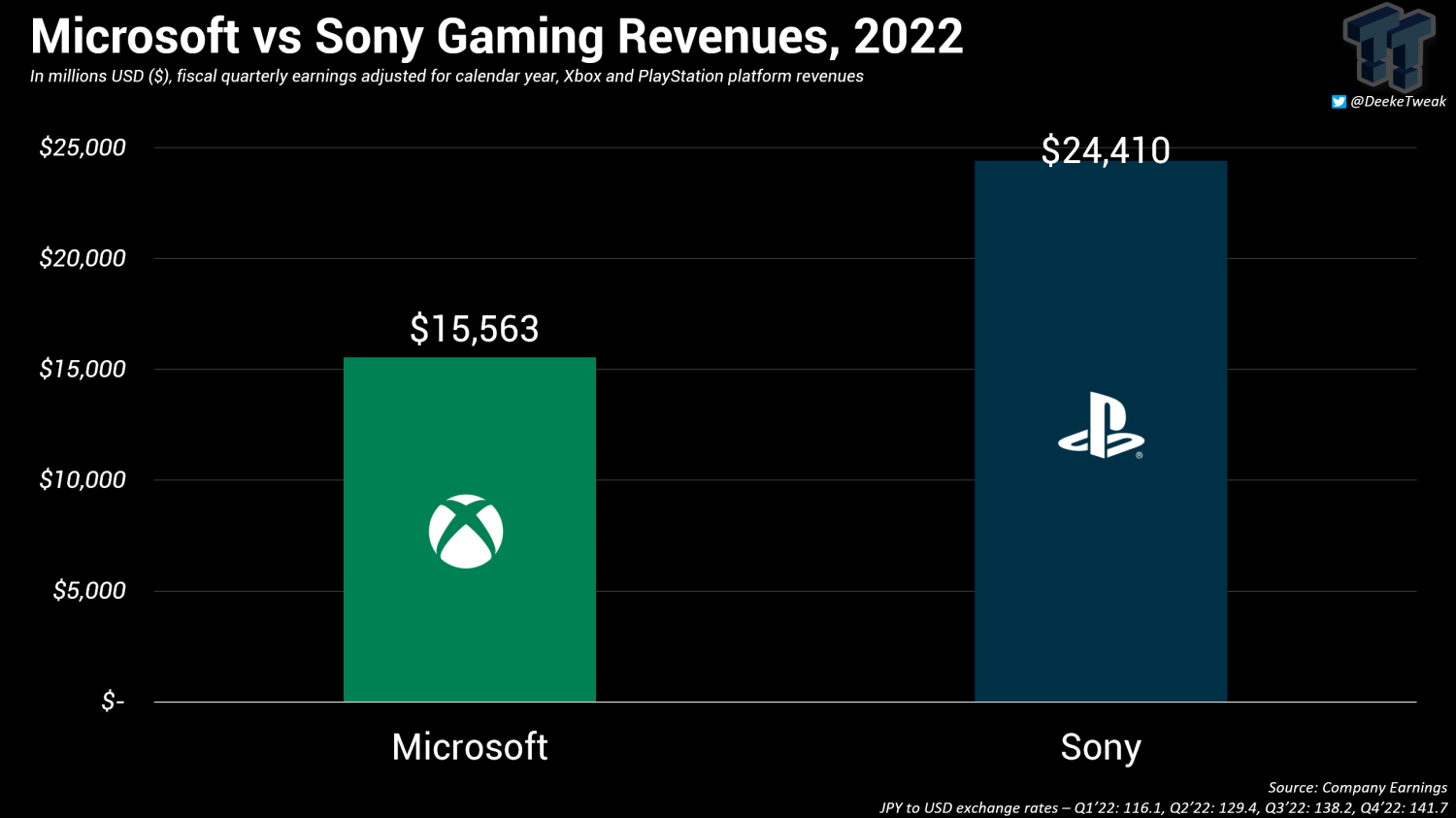
- Additionally, Sony has a significant presence in the video game industry with its PlayStation console series, which continues to be a major player in the market.
Sony\"s journey from its foundation to the present day marks a story of innovation, diversification, and adaptation to changing market dynamics, securing its place as a leader in various industry sectors.

History of Sony
Dive into the fascinating world of technology and discover the endless possibilities it offers. From the latest gadgets to groundbreaking inventions, this video is a tech enthusiast\'s dream come true. Get ready to be amazed!
Origins of Sony
Embark on a journey of new beginnings and explore the transformative power they hold. This inspiring video will motivate you to embrace fresh starts, whether it\'s in your career, relationships, or personal growth. Discover the endless opportunities that await you!
Sony\"s Impact and Legacy
Sony, established in 1946 as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo and later renamed in 1958, has left an indelible mark on the technology and entertainment industries. Its journey from a small electronics shop to a global conglomerate is a story of innovation, resilience, and transformation.
- Sony\"s early products, including voltmeters and sound generators, paved the way for a series of groundbreaking consumer electronics. Notably, its first major consumer item was an audio tape recorder introduced in 1950.
- The company\"s innovation streak continued with the introduction of the first pocket-sized transistor radio in 1957, revolutionizing portable entertainment.
- In 1969, Sony changed the landscape of home entertainment with its color videocassette recorder, followed by the iconic Walkman portable tape player in 1979, altering how people listened to music on the go.
- The release of the PlayStation video game console in 1994 marked Sony\"s foray into the gaming industry, creating a cultural phenomenon that continues to influence gaming today.
- Sony\"s entertainment divisions, including Columbia TriStar and Sony Pictures, along with recording labels like Epic and Columbia, have made significant contributions to the film and music industries.
- Akio Morita, co-founder of Sony, was not just a business leader but also a visionary who helped shape Sony\"s innovative culture and global outreach.
Sony\"s journey reflects its ability to foresee and adapt to market needs, continuously innovating and venturing into new territories. Its impact extends beyond its products, influencing lifestyles, entertainment, and the global technology landscape.
Explore the dynamic journey of Sony, a beacon of innovation and transformation in the tech and entertainment world, shaping modern lifestyles and defining industry standards globally. Discover Sony\"s inspiring story of resilience, creativity, and global impact.